‘Devi Remains My Favourite Film, My Favourite Performance’
As Satyajit Ray’s Devi completes sixty years, Sharmila Tagore goes back in time to recall shooting for it and why its take on ignorance and blind religious superstition continues to be relevant even today…
I was thirteen when I first met Satyajit Ray. I called him Manik-da, as did others who knew him well. He introduced me to this wonderful world of cinema. He was my mentor.
My first film was Apur Sansar, where I played Aparna, the child bride of Apu. Though the film made me a household name in Bengal, it came at a cost. I was asked to leave my school. The principal of the Bengali-medium school I studied in felt that I would be a bad influence on my fellow students.
When my father’s efforts to make her change her mind fell on deaf ears, he grandly proclaimed that working in a Ray film was a huge honour and he would prefer his daughter to be part of a Ray film than carry on in a school which did not appreciate this. It was an opportunity of a lifetime, he insisted.
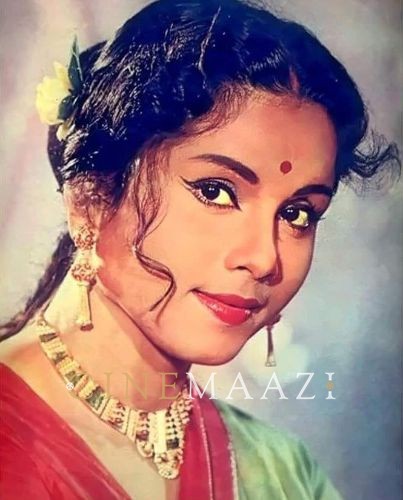
It was during the summer vacations the next year that Manik-da called me again for another film. This time for Devi. I was fourteen at that time. It was made in 1959. Today, so many years, so many films later, it remains my favourite film, my favourite performance. Even the subject, set in 1860, in my opinion remains so relevant today.
In the second half of the nineteenth century, the period in which Devi is set, the confrontation between Hindu orthodoxy and rational reformism was at its most intense. The conflict had permeated the zamindar class and many young reformers, in fact, came from this class.

Yet, that this reformist voice wasn’t yet strong enough to stand up to the entrenched dogmatic beliefs and bigotry is clear, when he is called back urgently by his sister-in-law. The chanting priests, the fervent crowd of worshippers and his father’s will hold him at bay.
Harisundari, the elder daughter-in-law, stands somewhere in the middle. She is a rational woman, yet unable to let go of centuries of orthodox conditioning.
When I read the script this time, I realized what an opportunity it would offer me in terms of performing. As far as I can discern, there isn’t a false note in the film, the assured way in which it moves to the shattering climax, the haunting music, the cinematography which heightens the mood of impending doom.
The opening shots reveal the fervid religiosity of the zamindar, Kalikinkar, almost setting the mood for what is to unfold. As the zamindar watches the Durga Puja as if in a trance, the incense shrouding the air, the cymbals and the drum on the soundtrack, it is impossible not to have a feeling of unease. One is immediately aware that one is in the presence of one intoxicated by faith.

Just watch the scene where the father-in-law comes running to Doyamoyee, muttering ‘Ma, ma’, after his dream where he sees Doya’s face and eyes morph into that of the goddess. He falls at Doya’s feet in abject worship, to be followed by Doya’s brother-in-law.
The revulsion and fear that Doya experiences is depicted not by traditional cinematic forms. One sees her nails digging into the wall next to her even as her toes curl away and you know she is revolted by the spectacle, her very being brutalized and shrinking, a feeling that as a viewer I feel when I watch the film sixty years on.
In the absence of her Western-educated husband who stays in Calcutta, Doya is simply not strong enough to resist the fanatic will of the father-in-law. She is as much a victim of the patriarchal set-up in which she has grown up, where she has been taught not to question what is asked of her by the elders of the house. Even as she is garlanded and dressed up as goddess, one needs just a look at her face to know that she is full of doubts, though too timid, too tradition bound, too young to assert her will of self-preservation. It is not long before the relentless assault of being worshipped disturbs her sense of reality as Ray proceeds to unfold the doom that is now Doya’s fate.

The film was widely misinterpreted in the West at the time. While everyone in Bengal is familiar with Kali worship and is aware of the nature of the orthodox family structure and its dos and don’ts, the Western audience was not, and therefore experienced a great deal of difficulty in following the course of events, as the development of the plot grows out of this orthodox Bengali nature of the theme.
Even in India, there was a lot of trouble at the time of its release. The film became quite controversial as it was seen as an attack on Hinduism. The communist government of the time also seemed unwilling to promote a film that talked of what they deemed was outmoded superstition.
More so, because Ray was a Brahmo, it was hinted that he had chosen the subject to attack Hinduism, which was not true at all. Manik-da had to clarify that the film was against the orthodoxy of religion and not against Hinduism per se.
If anything, the subject remains relevant even now, with dark pockets of ignorance and superstition still prevalent, not to speak of a societal order made by men where women are mere tools and end up as helpless victims.
For one, in large sections of the population, a woman remains captive, she has no escape, no option. Two, she is mentally conditioned that whatever your family decides for you is the best for you, you are there to serve the family, you cannot have a mind of your own.
In Devi, even when Umaprasad urges Doyamoyee to accompany him to Calcutta, she is unwilling to do so, thinking about her father-in-law, about the child. And even towards the end, she fails to let go of the myth of incarnation only because she is afraid that it might bring bad luck to her husband, as she says, ‘Jodi ami devi hoi, tomar jodi amangal hoy’ (if I am Devi and bad luck befalls you).
This thinking exists even now and religious dogmas kind of reinforce these. So, Devi continues to be important in the way it addresses the use of religious orthodoxy to victimize the woman. Underlying this is the need for education, the kind of education that fosters rational thinking, which saves us from the darkness of ignorance and takes us forward towards a more enlightened future. An issue that Ray, like Tagore, believed in and which informs both Apur Sansar and Devi.
Till such time that religion is used to perpetuate ignorance and superstition, till such time that the true tolerant, progressive nature of religion continues to elude mankind, Devi will remain extremely significant and a must-see for anyone who loves meaningful cinema.
Tags
About the Author

Sharmila Tagore is one of the most iconic actresses of Indian cinema. Making her debut at the age of 15 in Satyajit Ray's Apur Sansar (1959), she went on to be the star of hugely successful films like Kashmir Ki Kali (1964), An Evening in Paris (1967), Aradhana (1969), Safar (1970), and Amar Prem (1972). She earned great acclaim for her performances in films like Devi (1960), Nayak (1966), Anupama (1966), Mississippi Masala (1991), Shubho Mahurat (2003), Abar Aranye (2003), and Antaheen (2009). She won the National Award for her performance in Mausam (1975). She has served as the Chairperson of CBFC, as well as an UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador. She has served as a jury member for prestigious film festivals like Cannes. She was awarded the Padma Bhushan in 2013.






.jpg)


